Ch. 16 Carboxylic Acids and Esters – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
-COOH
answer
Which functional group is a carboxylic acid?
question
-oic acid
answer
A carboxylic acid is named in the IUPAC system by replacing the -e in the name of the parent alkane with
question
What is the common name of the compound below?
answer
butyric acid
question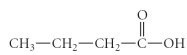
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
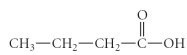
answer
butanoic acid
question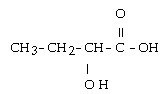
In the compound below, the hydroxyl group is in which position as noted by the common system?
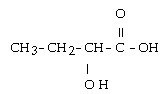
answer
?
question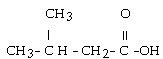
What is the IUPAC name for this compound?
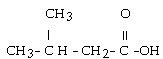
answer
3-methylbutanoic acid
question
What is the method of preparing carboxylic acids from alcohols or aldehydes?
answer
oxidation
question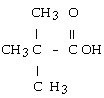
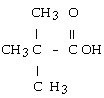
answer
The structural formula of the carboxylic acid produced by the oxidation of 2,2-dimethyl-1-propanol is
question
What kind of intermolecular bonding occurs between carboxylic acids?
answer
hydrogen bonding
question
Why do carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than similar alcohols or aldehydes?
answer
They form dimers that are relatively stable.
question
What happens to water solubility as chain length increases in carboxylic acids?
answer
it decreases
question
Carboxylic acids are __________ than sulfuric acid.
answer
weaker
question

answer
Which of the following is the reaction for the ionization of ?-hydroxypropanoic acid in water?
question
sodium formate and H2O
answer
The neutralization of formic acid by NaOH produces
question

answer
Which of the following is the reaction for the neutralization of ?-hydroxybutyric acid with NaOH?
question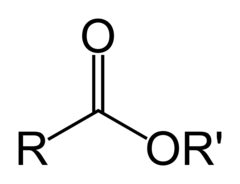
This functional group is known as a(n)

answer
ester
question
a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
answer
The reactants that will form an ester in the presence of an acid catalyst are
question
ethyl pentanoate
answer
What is the product of the reaction of pentanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of a strong acid?
question
1-propanol and ethanoic acid
answer
The alcohol and carboxylic acid required to form propyl ethanoate are
question
the alcohol
answer
From what component is the first part of the name of an ester (such as methyl acetate) derived?
question
What is the common name of this compound?
answer
ethyl acetate
question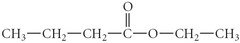
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
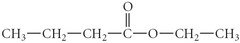
answer
ethyl butanoate
question
the hydrophobic end
answer
Which part of a soap is responsible for its ability to dissolve fats and oily dirt?
question
1. The parent chain is the longest chain that includes the carbon atom of the carbonyl group 2. Name the parent chain by changing the -e ending of the corresponding alkane name to -al 3. number the parent chain by assigning the #1 to the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group but this number is not given in the name 4. Find and number the substituents, always giving the lowest number possible 5. When the aldehyde functional group is attached to a carbon ring, name the ring and add the suffix -carbaldehyde
answer
Naming Aldehydes
question
1. The parent is the longest chain that includes the carbon atom of the carbonyl group 2. Name the parent chain by changing the -e ending of the corresponding alkane name to one 3. Number the parent chain so that the carbonyl carbon receives the lowest possible number - Position of carbonyl carbon is shown by placing the number right before the parent name, like 2-hexanone 4. Find and number the substituents, they go in front of the parent and we always assign the lowest number possible 5. Cyclic ketones are named by giving the name of the carbon ring and adding the suffix -one. We don' t add the #1
answer
Naming Ketones
question
Intermediate between those of alcohols and alkanes of similar molecular mass Have higher boiling points than alkanes because of the dipole-dipole attractions between carbonyl groups in these molecules
answer
Boiling Points of Aldehydes and Ketones
question
Aldehydes and ketones that have 5 carbons or less are soluble in both organic solvents and water Aldehydes and ketones with longer carbon chains are not soluble in water but they are soluble in organic solvents
answer
Solubility
question
Tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones -An aqueous solution of AgNO3 (Ag+ is the oxidizing agent) and NH3 is added to the unknown compound. If a silver "mirror" is seen on the inside of the test tube this means you have an aldehyde compound. If you do not see the silver mirror then your compound is (probably) a ketone.
answer
Tollens Test
question
Aldehyde reduction produces a primary alcohol Ketone reduction produces a secondary alcohol
answer
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
question
When H2 is added to an aldehyde a primary alcohol is formed When H2 is added to a ketone a secondary alcohol is formed
answer
Hydrogenation Reaction
question
Turns to Carboxylic Acids. ADD O
answer
Oxidation of Aldehydes to Form Carboxylic Acids
question
Double bond removed from o and h and becomes oh - Primary alcohol. H should be left to oxidise to an acid. Add H2
answer
Reduction of Aldehydes to Form Primary Alcohols
question
Becomes alchohols. Alcohols are OH no double bond . Add H2
answer
Reduction of Ketones to Form Secondary Alcohols
question
Hemiacetal - o-ch3 one and oh replaces double bond. Acetal - two o- ch3
answer
Addition of Alchohols to Form Hemiacetals and Acetals
question
+H20 OH BECOMES O- + H30
answer
Dissociation of a Carboxylic Acid in Water
question
+ NaOH OH becomes C - O- NA+ + H20
answer
Neutralization of a Carboxylic Acid
question
Making an Ester + HO - CH3 CH3 - C - O - CH3
answer
Esterification: Carboxylic Acid and an Alcohol
question
+ H - OH Breaking apart the bond O becomes - OH + HO - CH3
answer
Acid Hydrolysis of an Ester
question
+ NaOH O becomes o- Na+ + HO - CH3
answer
Base Hydrolysis of an Ester ( Saponification )
question
The IUPAC name of a carboxylic acid is obtained by replacing the e in the corresponding alkane name with oic acid.
answer
Naming Carboxylic Acids
question
Step 1 : Write the name for the carbon chain from the alcohol as an alkyl group. Step 2: Change the ic acid of the acid name to ate.
answer
Naming Esters
question
Monosaccharides and Disaccharides
answer
What are simple sugars?
question
Polysaccharides
answer
What are complex sugars?
question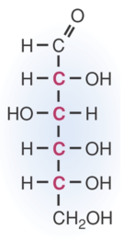

answer
Straight Chain Structure of Glucose
question
a-D-Glucose
answer
Haworth Projections - Cyclc Ring Form of Glucose
question
- Right = D isomer - Left = L isomer
answer
Explain the types of carbohydrate isomer based on their alcohol (OH) group bonded to only or last asymmetric carbon atom
question
The OH is drawn up on a ring structure
answer
Beta-anomer
question
The OH is drawn down on a ring structure
answer
Alpha-anomer
question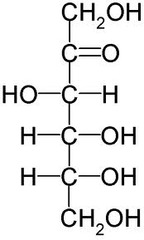

answer
Straight Chain Structure of Fructose
question
D-Glucitol --> D-Glucose --> D-Gluconic Acid
answer
Oxidation and Reduction of Monosaccharides
question
Glucose + Glucose
answer
Maltose
question
Glucose + galactose
answer
Lactose
question
Glucose + Fructose
answer
Sucrose
question
Amylose - a(1-;4) glycosidic bonds Amylopecting a(1-->6) glycosidic bonds or a(1->4) glycosidic bonds
answer
Starch
question
animal starch is a polymer of glucose that is stored in the liver and muscle of animals. a(1-->6) glycosidic bonds or a(1->4) glycosidic bonds.
answer
Glycogen
question
is the major structural material of wood and plants. Humans cannot break down Bcellulose but a cellulose . B(1-->4) GLYCOSIDIC BONDS . Unbranched polysaccharide.
answer
Cellulose
question
aldehyde and 5
answer
aldopentose
question
ketone and 5
answer
ketopentose
question
aldehyde and 6
answer
aldohexose
question
ketone and 6
answer
ketohexose



